DEVELOPMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND DIGITAL INFRASTRUCTURE IN AFRICA
The Beijing Summit of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) in September 2024 marked a transformative step in digital collaboration between China and Africa. Recognizing the growing importance of digital technology in economic development, Chinese President Xi Jinping announced the establishment of a Digital Technology Cooperation Center and the launch of 20 digital demonstration projects. These initiatives aim to harness cutting-edge technological advancements and industrial transformation to strengthen Africa’s digital ecosystem.
In July 2024, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) of China, alongside 26 African nations, introduced the China-Africa Action Plan for Digital Cooperation and Development. This comprehensive framework outlines six critical pillars: digital policy, digital infrastructure, digital innovation, digital transformation, digital security, and digital capabilities. By focusing on these key areas, the plan seeks to bridge Africa’s digital divide, enhance cyber resilience, and drive innovation-driven economic growth.
To accelerate the implementation of the Action Plan, the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT) hosted a virtual seminar, “Outlook 2025 on China-Africa Digital Cooperation,” on March 18, 2025. The event brought together key stakeholders from diverse sectors, including telecommunications companies, financial institutions, policy makers, and research organisations. The discussions focused on enhancing mutual understanding, strengthening cooperation frameworks, and fostering strategic partnerships to ensure meaningful digital transformation across the continent.
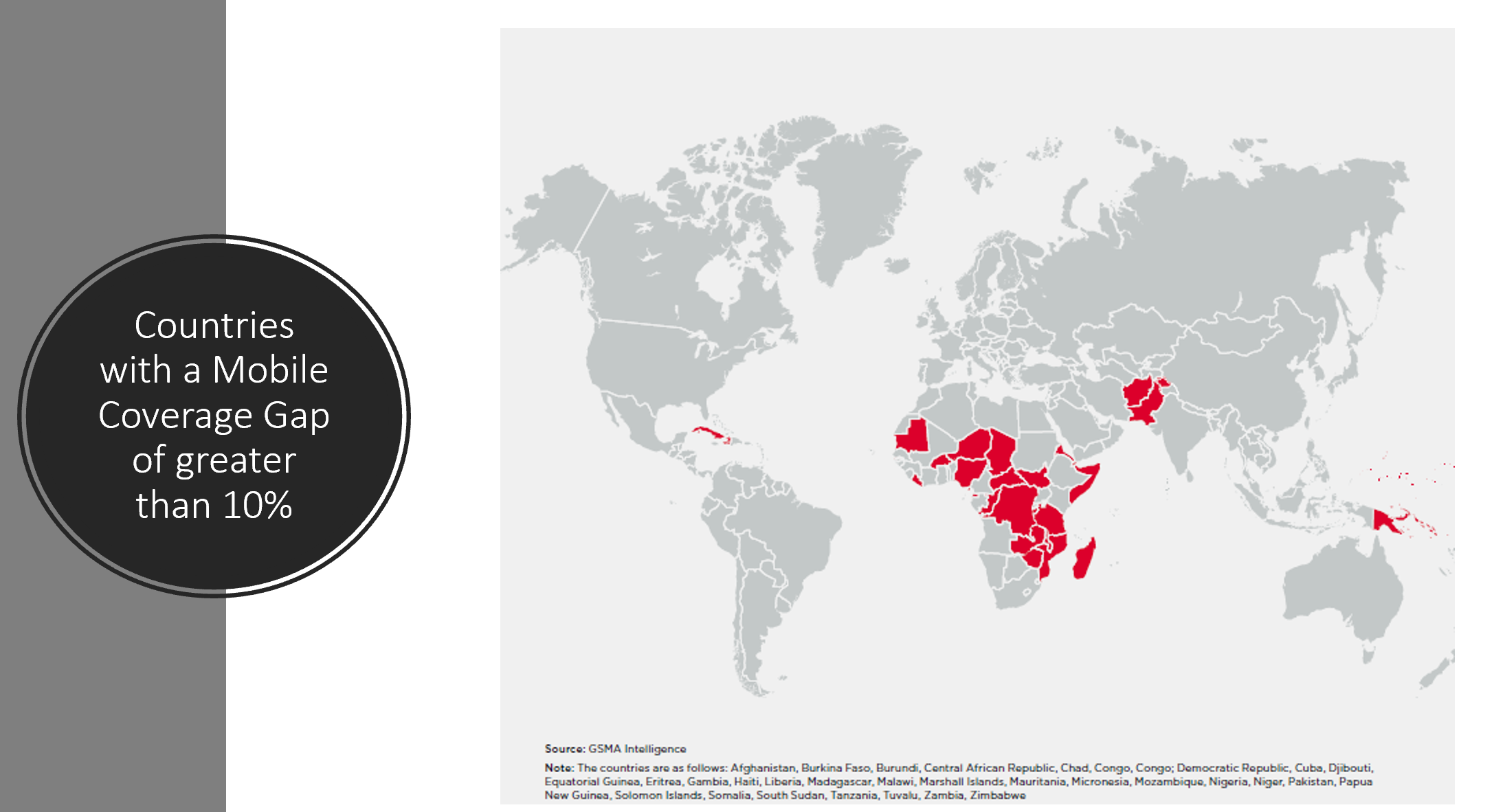
Speaking at the seminar, Mr. Leonard Mabele, Research & Innovation Lead at AFRALTI, provided an in-depth analysis of Africa’s rapidly evolving telecom infrastructure landscape. He highlighted the significant strides made in mobile and internet penetration, driven by a young and growing population and the increasing affordability of smartphones. However, he also pointed out the persistent challenges, including affordability barriers, digital skills shortages, and disparities in access between urban and rural communities. Additionally, he emphasised the critical role of accurate data collection in shaping policies and investments to address connectivity gaps effectively.
In addressing broadband infrastructure, Mabele underscored the superior potential of optical fibre technology as the foundation of future-proof broadband networks. Optical fibre offers unparalleled bandwidth, energy efficiency, and a lower carbon footprint, making it an essential component of Africa’s digital infrastructure. He also noted that Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) serves as a viable complementary solution, particularly in regions where fibre deployment remains limited. Market data from 2023 showed a 29.5% year-on-year growth in fibre deployment and a 21.3% increase in FWA adoption, signaling a strong shift towards high-speed connectivity solutions.
Another focal point of the seminar was the role of satellite technology, especially Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites, in providing connectivity to Africa’s most remote and underserved areas. With traditional fibre networks and mobile towers struggling to reach rural regions, LEO satellites offer a promising alternative, though challenges such as high costs and regulatory hurdles must still be addressed.
Beyond infrastructure, technological innovation is unlocking new opportunities across various sectors. Private sector investments in Internet of Things (IoT) solutions are accelerating, particularly in agriculture, energy, and water resource management. The emergence of Artificial Intelligence (A.I) applications is also transforming key industries, including healthcare, telemedicine, education, and disaster response. However, Mabele stressed that achieving a truly inclusive digital transformation requires greater emphasis on digital literacy and skills training, ensuring that Africa’s workforce is prepared for the evolving demands of the digital economy.
Looking ahead, stakeholders must prioritize policy harmonization, infrastructure investments, and capacity-building initiatives to sustain Africa’s digital progress. Collaborative partnerships between governments, private enterprises, and development organisations will be essential in fostering an innovative, inclusive, and secure digital environment. Through shared expertise and strategic alliances, China and Africa can collectively harness the power of digital technology to drive economic resilience, empower communities, and secure a future of widespread connectivity and innovation.



